| Aspect | Development Server | Stage Server | Preproduction Server |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Active development and debugging of features | Feature and functionality testing | Production-readiness validation |
| Configuration | Loosely configured, may not mimic production | Similar to production, but not exact | Identical to production |
| Data | Mock data, test data, or local databases | Mock or sanitized data | Real or anonymized production data |
| Testing | Unit tests, local integration tests | Functional, UI, and regression testing | Performance, load, and end-to-end testing |
| Access | Developers only | Developers, QA, and stakeholders | Operations, release teams, and performance testers |
| Changes Allowed | Frequent, active debugging and code changes | Flexible (debugging permitted) | Locked down (minor fixes only) |
| Deployment Frequency | Continuous (frequent builds) | Regular updates during the testing phase | Rare, only near final release |
| Tools/Processes | Local development tools, CI/CD pipelines | Testing frameworks, bug tracking tools | Monitoring tools, deployment scripts |
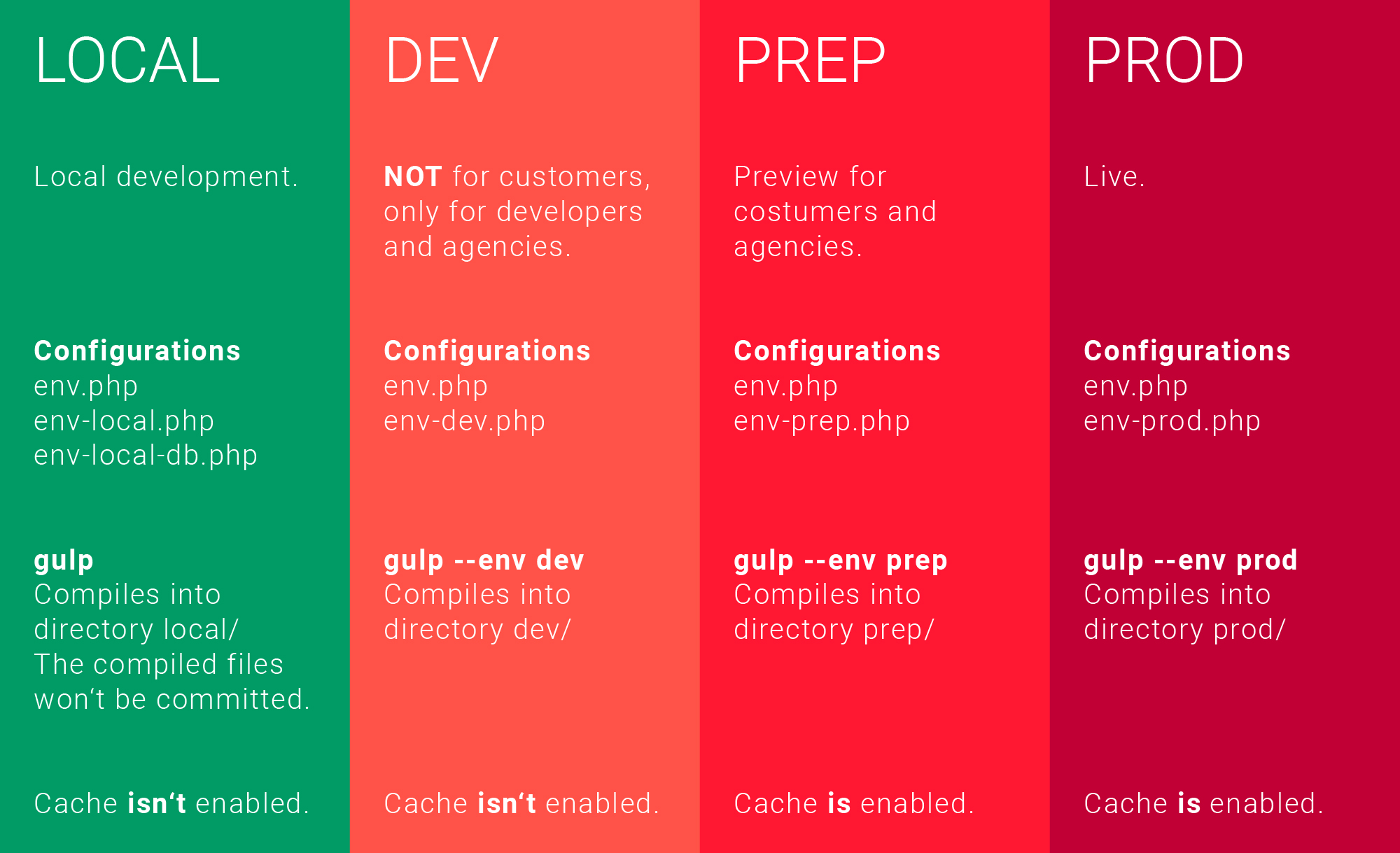
Setup reacat app:
.env.development
.env.staging
.env.production
npm run build # uses production
NODE_ENV=staging npm run build
Option 2 (better for containers - docker, kubernetes): Runtime environment variables
public/config.json
{
"apiUrl": "https://prod.example.com"
}
fetch('/config.json')
.then(r => r.json())
.then(config => {
window.APP_CONFIG = config;
// render app here
});
window.APP_CONFIG.apiUrl
Option 3: Inject env variables via the hosting server (Nginx, Node)
<script src="/env.js"></script>
window.env = {
API_URL: "https://prod.example.com"
};
window.env.API_URL